Windows; Windows 7; Search Community member; SU. Created on February 27, 2018. Download driver for CsrBtPortEnumeratedDevice00.
- Csrbtport_enumerated_device_00 Driver Windows 7
- Windows 7 Download
- Csrbtport_enumerated_device_00 Windows 7 10
- Windows 7 Free Download
Bluetooth Radio Reset and Recovery is a technology in Windows 10, version 1803 and later that introduces a robust reset and recovery mechanism for Bluetooth radios. This mechanism enables Bluetooth radios to recover from hardware failures that lead to malfunction, loss of connectivity, or unresponsiveness to operational commands. The goal is to automatically recover the radio, making the user experience seamless and reducing the likelihood of requiring a system restart.
Bluetooth radio reset and recovery can be implemented with or without firmware dependencies. IHV or OEM partners can extend the software-based reset mechanisms available on all Windows PCs with supported device- or firmware-level reset mechanisms to increase the likelihood of successful recovery.
- CSR Bluetooth dongle does NOT work, even updated with latest windows 7 driver or driver from manufacture OK I've tried TWO Bluetooth dongle, both with CSR chipset and I'm stuck. Basically I just bought new Microsoft Wedge Mobile keyboard along with Wedge touch mouse, both are Bluetooth devices.
- Update: Please download Toshiba Bluetooth stack driver it will connect your device automatically.Download it hereToshiba Bluetooth stack https://bit.ly/2T.
- Parts: 45 days money-back and 12-month, worry-free Guarantee! Labor: 45 days money-back and 12-month, worry-free Guarantee! Free Download Microsoft Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR USB Device Driver 6.2.0.2600 for Vista64/Windows 7 x64 (Bluetooth) SOFTPEDIA. Windows 7 64 bit. I'm using a CSR Harmony Bluetooth 4.0 USB adapter on my Windows 7 64-bit computer.
- Then Windows tries and fails to find drivers with the error: csrbtportenumerateddevice00 No Driver Found. The device is also listed like that in Device Manager. Because there are no drivers, the device is not listed in the RealTek playback devices dialogue and the headphones obviously don't work.
Important
This topic is for developers. If you are a customer experiencing bluetooth problems see Fix Bluetooth problems in Windows 10.

Bluetooth Reset and Recovery Scenarios
There are three broad categories of issues where Bluetooth Reset and Recovery is initiated:
Bus enumeration failures: The radio fails enumeration or re-enumeration by the underlying bus (for Bluetooth, this is typically USB or UART) as indicated by a visible failed state (yellow bang) in Device Manager, which may be symptomatic of underlying hardware errors.
Driver enumeration failures: The Bluetooth radio is in a failed state after successful enumeration by the underlying bus. This typically occurs when building up the driver stack for the radio, e.g. when a filter or function driver is installed on the Bluetooth radio device node (devnode). Failures could occur if a driver encounters an error during one or more start operations and as a result reports a PnP failure. An example of such an operation could be a firmware download to the device.
Non-enumeration failures: The device is not in a failed state but is otherwise non-operational as seen by the driver stack. These are failures outside of the enumeration pathway and could be general critical transport-specific failures or device-specific failures such as a catastrophic firmware error. The Bluetooth Reset and Recovery mechanisms described below are used in these cases.
Reset and Recovery Mechanisms
While there are different approaches to recover from a failed state, Bluetooth uses a standardized ACPI-based recovery mechanism to attempt to restore the radio to a working state.
GUID_DEVICE_RESET_INTERFACE_STANDARD defines two levels of reset. Note that:
The reset mechanisms work only for internal devices so externally-pluggable Bluetooth radios such as dongles are not supported.
The reset mechanisms require support both in Windows (typically by the function driver stack) and the underlying firmware (typically in the ACPI BIOS) to actually perform the reset.
The actual reset mechanism is system-specific.
| Reset Level | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Function-level device reset (FLDR) | The reset operation is restricted to a specific device and is not visible to other devices. There is no re-enumeration. Function drivers must assume that the hardware has returned to its original state after the operation. Intermediary state is not preserved. |
| Platform-level device reset (PLDR) | The reset operation affects a specific device and all other devices that are connected to it via the same power rail or reset line. The reset operation causes the device to be reported as missing from the bus and re-enumerated. This type of reset has the most impact on the system since all devices that share the resource go back to their original state. |
To support FLDR there must be an __RST method defined within the _ADR namespace as detailed in ACPI firmware: Function-level reset.
To support PLDR there must be an _RST or _PR3 method defined within the _ADR namespace as detailed in ACPI firmware: Platform-level reset. Note that if a _PR3 method is used, ACPI uses the D3Cold power cycle mechanism to reset. This emulates removing power from the device and subsequently restoring it. If any other devices share the same power rail they will also be reset. If an _RST method is defined and referenced by a _PRR (PowerResource) then all devices that use that PowerResource will be affected.
Since PLDR works only for internal devices, it must be declared as such in ACPI. For USB devices, to specify a port that is internal (not user visible) and can be connected to an integrated device, set the _UPC.PortIsConnectable byte to 0xFF and the _PLD.UserVisible bit to 0.
If the _PR3 (D3Cold) mechanism is used for PLDR, ensure that scenarios like SystemWake and DeviceWake continue to work. Nominally, this means that there are appropriate power resources defined for D2, e.g. _PR2. The following table is a useful guide:
| Power state | ACPI resource | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| D2 | _PR2 | Any power or clocks required for the class-defined reduced-functionality of this state. |
| D3 Hot (reqd.) | _PR2 | The same resources as the next higher state that is supported (D2, D1, or D0). |
| D3cold | _PR3 | Only the power or clocks required for the device to appear on its bus and respond to a bus-specific command. |
Related links
-->Bluetooth Radio Reset and Recovery is a technology in Windows 10, version 1803 and later that introduces a robust reset and recovery mechanism for Bluetooth radios. This mechanism enables Bluetooth radios to recover from hardware failures that lead to malfunction, loss of connectivity, or unresponsiveness to operational commands. The goal is to automatically recover the radio, making the user experience seamless and reducing the likelihood of requiring a system restart.
Bluetooth radio reset and recovery can be implemented with or without firmware dependencies. IHV or OEM partners can extend the software-based reset mechanisms available on all Windows PCs with supported device- or firmware-level reset mechanisms to increase the likelihood of successful recovery.
Important
This topic is for developers. If you are a customer experiencing bluetooth problems see Fix Bluetooth problems in Windows 10.

Bluetooth Reset and Recovery Scenarios
There are three broad categories of issues where Bluetooth Reset and Recovery is initiated:
Csrbtport_enumerated_device_00 Driver Windows 7
Bus enumeration failures: The radio fails enumeration or re-enumeration by the underlying bus (for Bluetooth, this is typically USB or UART) as indicated by a visible failed state (yellow bang) in Device Manager, which may be symptomatic of underlying hardware errors.
Driver enumeration failures: The Bluetooth radio is in a failed state after successful enumeration by the underlying bus. This typically occurs when building up the driver stack for the radio, e.g. when a filter or function driver is installed on the Bluetooth radio device node (devnode). Failures could occur if a driver encounters an error during one or more start operations and as a result reports a PnP failure. An example of such an operation could be a firmware download to the device.
Non-enumeration failures: The device is not in a failed state but is otherwise non-operational as seen by the driver stack. These are failures outside of the enumeration pathway and could be general critical transport-specific failures or device-specific failures such as a catastrophic firmware error. The Bluetooth Reset and Recovery mechanisms described below are used in these cases.
Reset and Recovery Mechanisms
While there are different approaches to recover from a failed state, Bluetooth uses a standardized ACPI-based recovery mechanism to attempt to restore the radio to a working state.
GUID_DEVICE_RESET_INTERFACE_STANDARD defines two levels of reset. Note that:
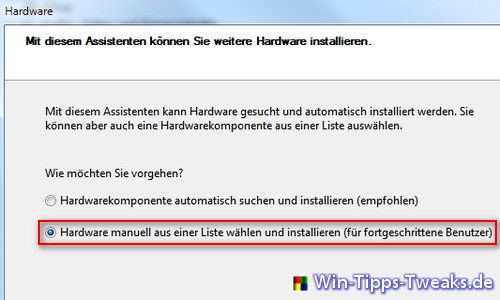
Windows 7 Download
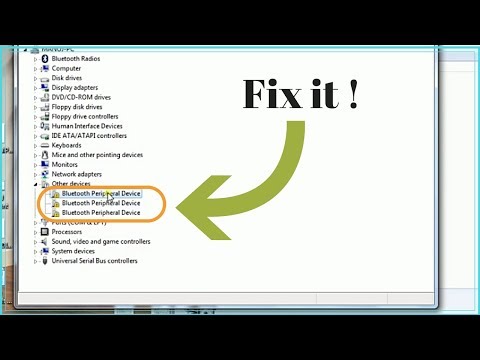
Csrbtport_enumerated_device_00 Windows 7 10
The reset mechanisms work only for internal devices so externally-pluggable Bluetooth radios such as dongles are not supported.
The reset mechanisms require support both in Windows (typically by the function driver stack) and the underlying firmware (typically in the ACPI BIOS) to actually perform the reset.
The actual reset mechanism is system-specific.
| Reset Level | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Function-level device reset (FLDR) | The reset operation is restricted to a specific device and is not visible to other devices. There is no re-enumeration. Function drivers must assume that the hardware has returned to its original state after the operation. Intermediary state is not preserved. |
| Platform-level device reset (PLDR) | The reset operation affects a specific device and all other devices that are connected to it via the same power rail or reset line. The reset operation causes the device to be reported as missing from the bus and re-enumerated. This type of reset has the most impact on the system since all devices that share the resource go back to their original state. |
To support FLDR there must be an __RST method defined within the _ADR namespace as detailed in ACPI firmware: Function-level reset.
To support PLDR there must be an _RST or _PR3 method defined within the _ADR namespace as detailed in ACPI firmware: Platform-level reset. Note that if a _PR3 method is used, ACPI uses the D3Cold power cycle mechanism to reset. This emulates removing power from the device and subsequently restoring it. If any other devices share the same power rail they will also be reset. If an _RST method is defined and referenced by a _PRR (PowerResource) then all devices that use that PowerResource will be affected.
Since PLDR works only for internal devices, it must be declared as such in ACPI. For USB devices, to specify a port that is internal (not user visible) and can be connected to an integrated device, set the _UPC.PortIsConnectable byte to 0xFF and the _PLD.UserVisible bit to 0.
If the _PR3 (D3Cold) mechanism is used for PLDR, ensure that scenarios like SystemWake and DeviceWake continue to work. Nominally, this means that there are appropriate power resources defined for D2, e.g. _PR2. The following table is a useful guide:
| Power state | ACPI resource | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| D2 | _PR2 | Any power or clocks required for the class-defined reduced-functionality of this state. |
| D3 Hot (reqd.) | _PR2 | The same resources as the next higher state that is supported (D2, D1, or D0). |
| D3cold | _PR3 | Only the power or clocks required for the device to appear on its bus and respond to a bus-specific command. |